
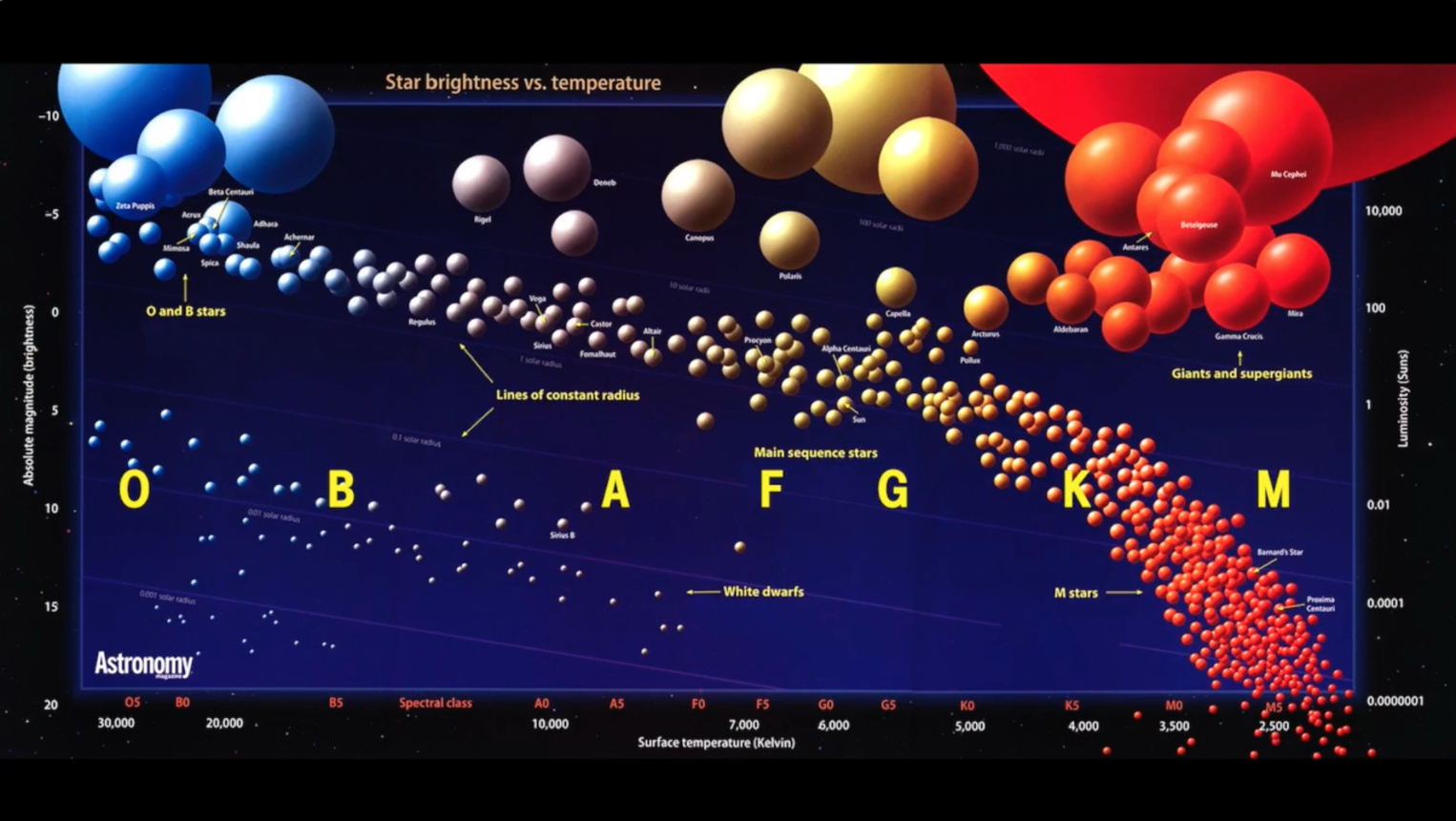

Like most other stars, they also are in a state of equilibrium in which gravity is balanced by gas pressure at each radius, and the luminosity flowing outwards at each level is balanced by the energy generated interior to that level. Through theoretical modeling of the Sun and other main sequence stars, scientists have determined that the factor that differentiates them from the three other types of stars is the fact that their energy is generated internally by the conversion of hydrogen to helium (giants and supergiants produce their energy by gravitational contraction and by converting helium to even heavier elements white dwarfs are like dying embers in a fireplace, radiating away their store of heat energy). The Sun is a main sequence star and thus, by implication, all other main sequence stars must share its fundamental nature. The fact that the main sequence stars are represented by a band across the HR diagram that is smoothly populated from the rare O and B stars to the very common M stars strongly suggests that these stars are physically the same type of object, though some factor must be responsible for their range in observable properties.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
